Why it is important to educate your audience and how to do it
I often hear it from different people: “I don’t have money for content marketing”, “We already tried to run a blog, but it didn’t work”, “I’d rather buy more paid advertising for this money”.
I think that it all depends on how exactly you do content marketing. I find the educational part of content marketing extremely important.
What’s why, in this article, I will tell you:
- Why it is important to educate your audience
- How educational content works for different business models
- How to create effective educational content
- What market education is and why you need it
What is market education and why do you need it?
Market education is a tactic that helps you get new customers and retain existing ones through teaching the audience.
You can give users information about the industry, ways to solve their problems, etc. For example, consulting companies make guides about industry trends, online courses make free short courses about new professions.
Awareness ladder shows how it works before purchase:
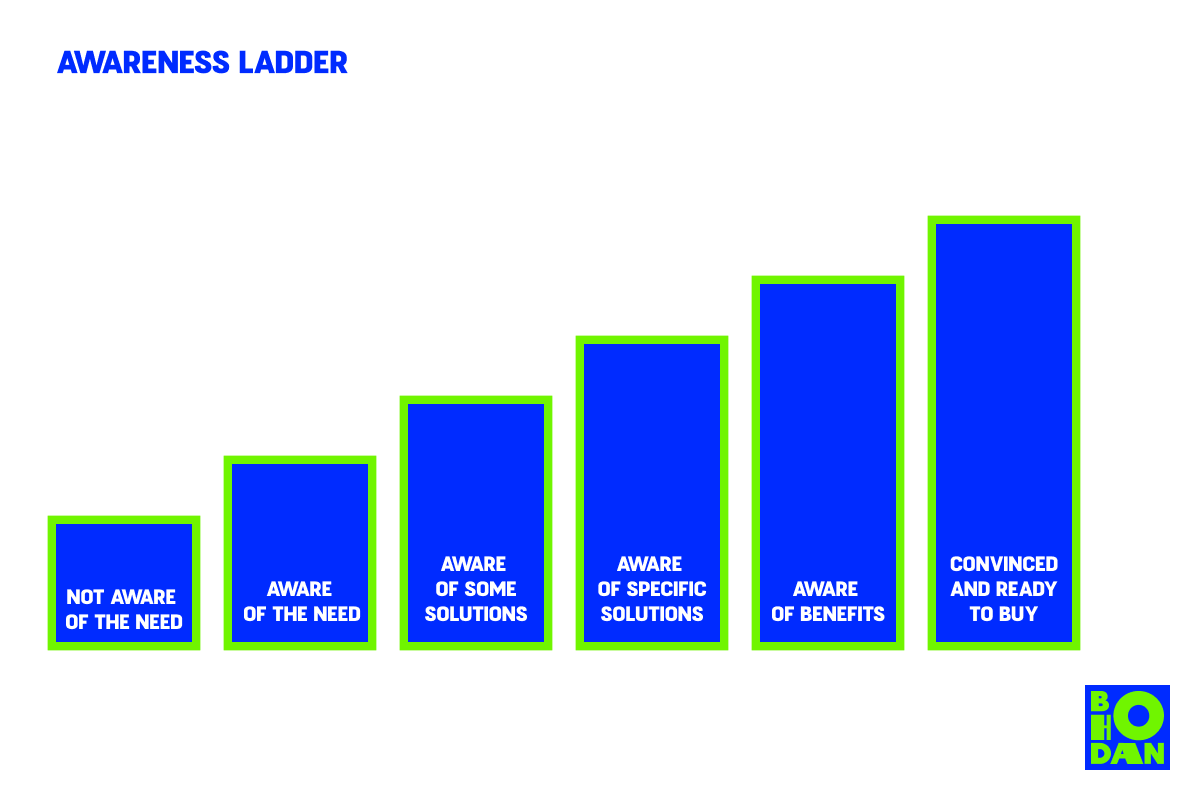
When users don’t recognize a problem, education highlights it. When users recognize the problem, education explains how to solve it and how the product may help.
All that increases perceived value of a product and decreases perceived price and friction.
But education works as well after purchase.
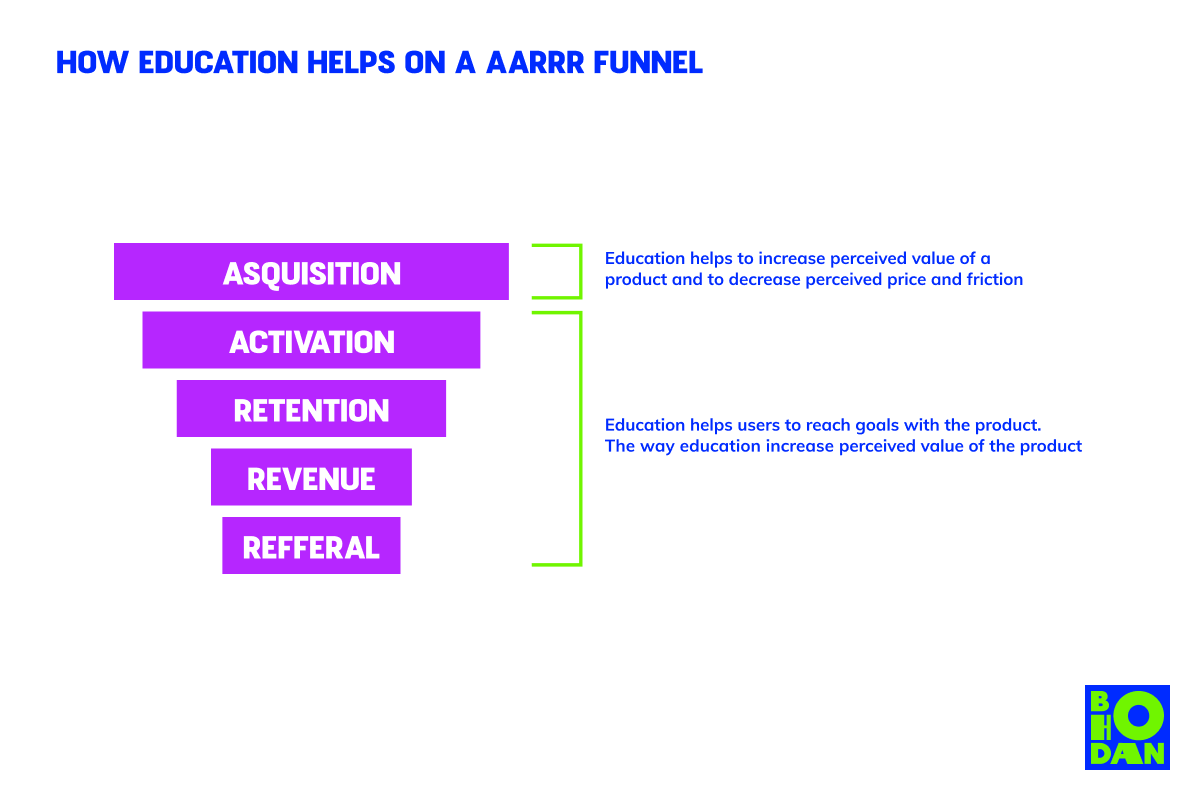
When users convert, education helps to activate them. After that, education helps to retain users.
Users are hiring products for a certain “job”. The more successful they are with reaching their goals, the more they might associate the success with using your product. That's why by additionally educating your users, you can make them more successful at reaching their goals and using your product.
Let’s take a look at how it works with different business models.
How does educational content work for different business models?
In this part, we will see how educational content works for subscription, usage-based model and revenue-share model.
Subscription
A subscription business model is a recurring revenue model in which customers pay a weekly, monthly, or yearly fee in exchange for your products or services.
It's getting more expensive over time to acquire new customers. Customer acquisition cost (CaC) keeps increasing and for most businesses, it's this way because of the rising advertising costs and more intense competition and market saturation over time.
So, if you have a subscription business model, your main priority is to keep retention high. It’s cheaper to keep current customers than to attract new ones.
You want to educate not only new users, but the current ones too. You want them to solve their problems better and have more success thanks to your product.

But it's not only about how long the users are retained, it's also about users being more successful in reaching their goals with your product.
If a customer churns after 1 year, but he is happy with the 'job' your product did — it's still a success. This customer reached his goals with your product. Now he is your brand ambassador.
Let’s dive into examples.
Often, SaaS create their own academies to teach users. For example, Ahrefs created open courses about SEO and business blogging with all the practice on Ahrefs tools.
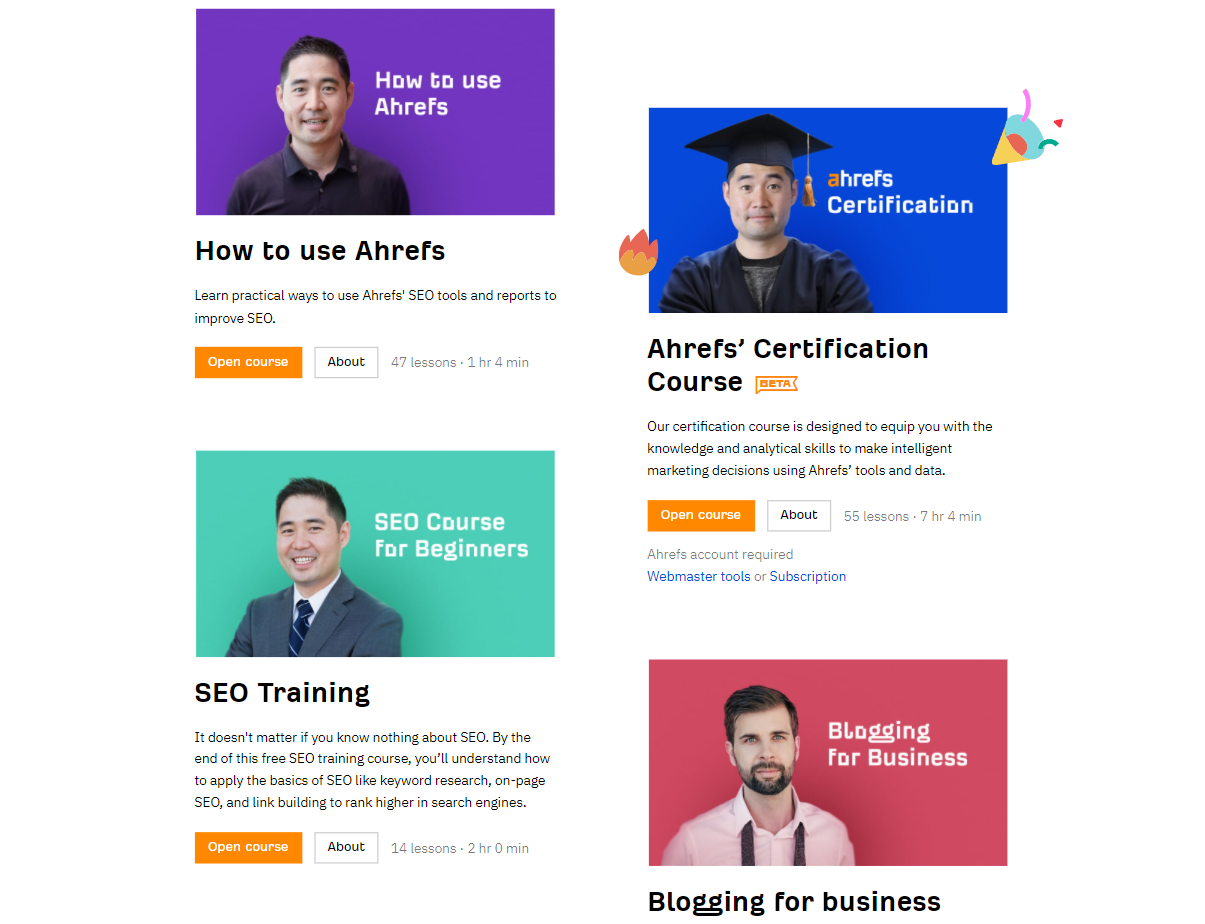
They also publish articles and guides for solving problems through Ahrefs.
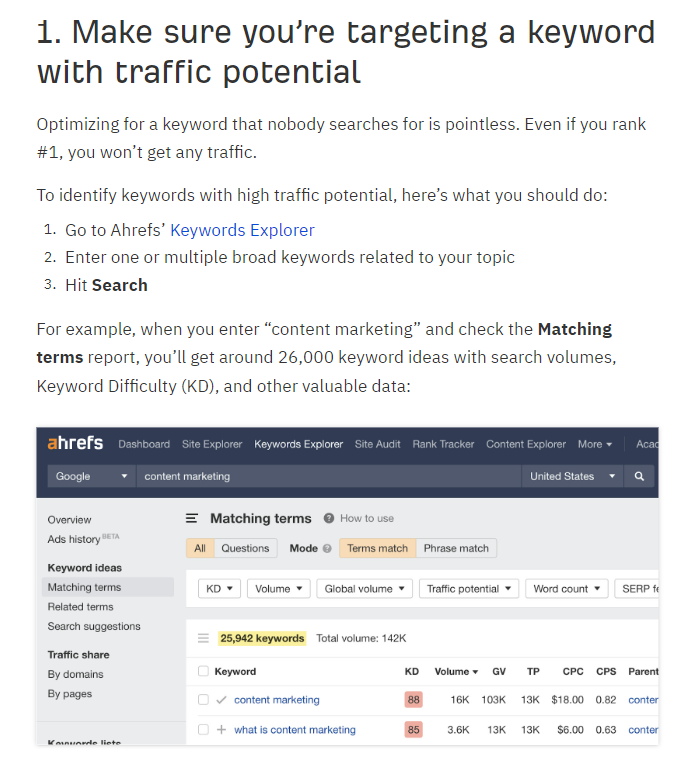
That’s a best practice in SaaS: to take a user’s problem and show how a good product can solve it. But the main thing here is not to just add your product, but to give value to the user.
That means:
- to give clear instructions about solving the problem
- to show different ways to solve the problem (not only using our product and maybe even referring to other products that can solve the problem better)
- to provide information about pitfalls
- to be honest (not to promise something they can’t give 100%)
Users see when a company wants to fool them. And that doesn’t make it more attractive for them - definitely not.
Let’s take a look at another example. Adobe doesn’t have online courses on its products. Instead, Adobe gives small lessons and tutorials. That can help users to get started.
But that’s only a small part of the Adobe educational content. Most of it is located on the YouTube channel, with more than 1 million subscribers. That’s logical — users often look for tutorials on YouTube.
You can use market education not only for B2B products, but also for B2C. HeadSpace provides users with articles about anxiety, sleep and mindfulness. This way, users can better understand their problems and, after that, solve these with free meditations from HeadSpace.
On most social networks, HeadSpace doesn’t post educational content, only supportive, but the YouTube channel also has educational playlists.
Usage-based model
Usage-based pricing is a SaaS pricing model that allows customers to pay for only what they use or consume. Billing occurs at the end of the billing cycle. In contrast, a subscription pricing plan is billed at a flat rate, regardless of how often they use the service.
There are lots of subscription-based SaaS products, the price of which also depends on how extensively the product is used, and once the company becomes more successful, they have to upgrade to more expensive plans.

Let’s see how such companies educate users. Customer data platform, Segment, suggests free courses, guides, case studies, reports and training for users.
There is only one difficulty. Users need to leave their emails to get access to educational content. This is how the company receives the user's emails.
Pendo uses a different approach. Users can read the first part of the content. If they want to see more, they should give contacts.
Along with using articles, white papers and guides, Pendo encourages users to sign up for a demo call.
Revenue-share model
Revenue-share model is a pricing model that allows customers to use a product for free and to pay only if they earn money with this product. In this case, the company takes a percentage from users’ outcomes.
So, it’s profitable for a company to educate users. The more a company educates users, the more successful users become and the more a company earns.

Adapty created an email course that helps app owners to improve app monetization.
Another example is Patreon. Patreon created a blog that helps creators start a membership and grow it.
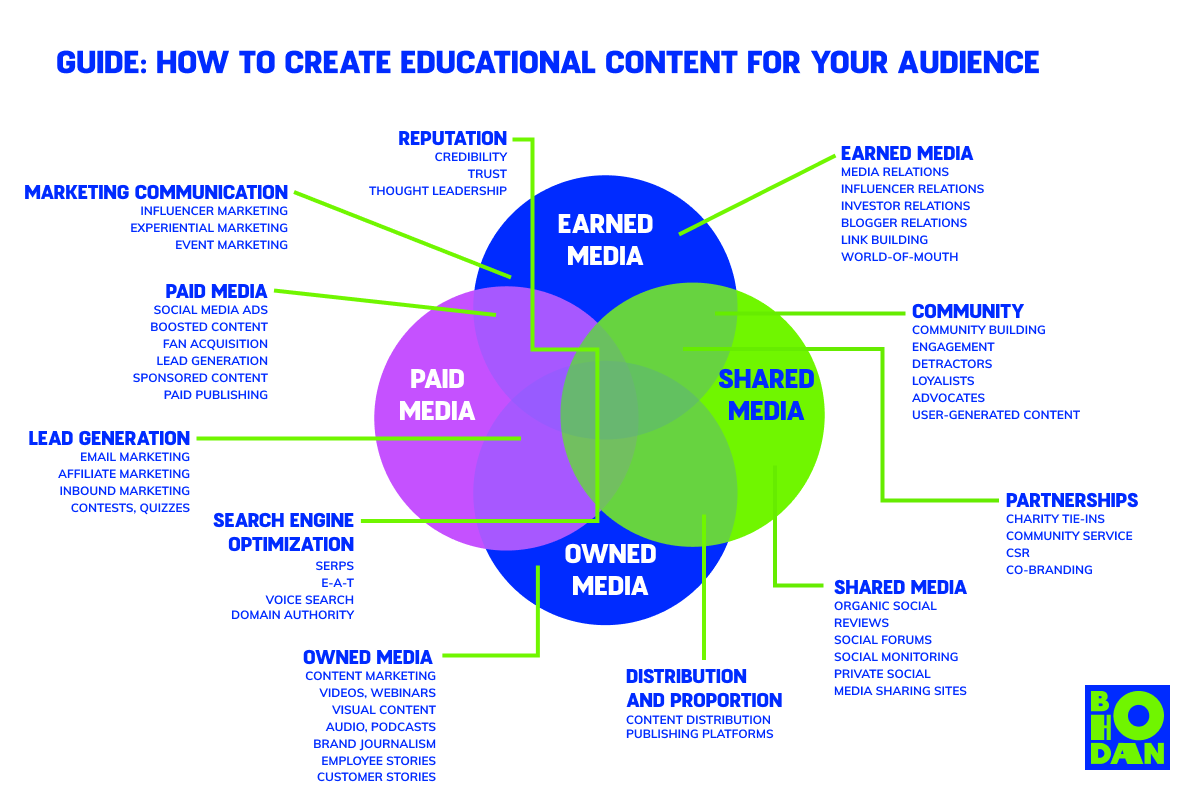
Want to read full article with the ultimate guide about educational content? Subscribe to my blog (it's free) 👇
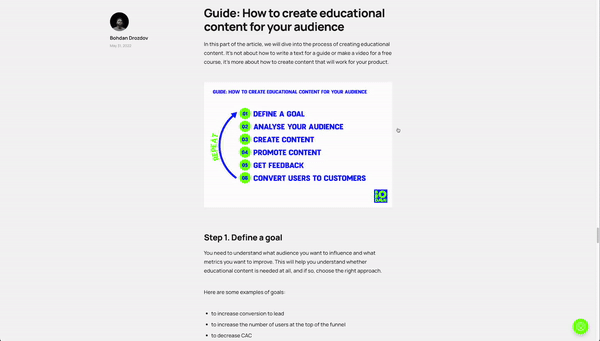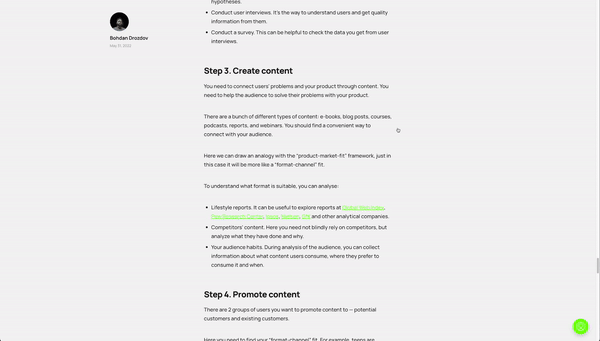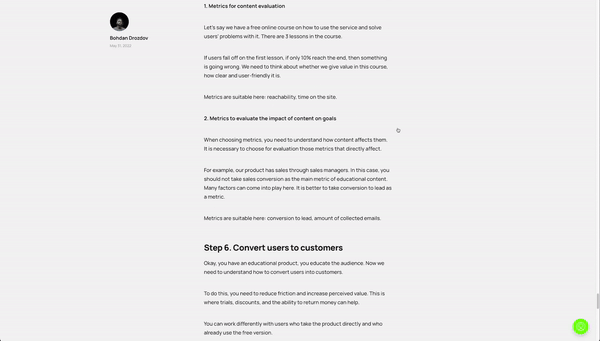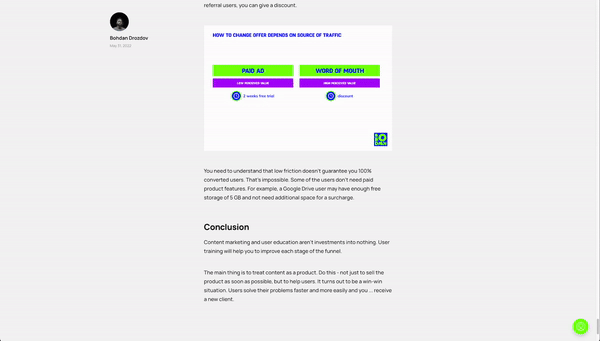
Guide: How to create educational content for your audience
In this part of the article, we will dive into the process of creating educational content. It’s not about how to write a text for a guide or make a video for a free course, it’s more about how to create content that will work for your product.

Step 1. Define a goal
You need to understand what audience you want to influence and what metrics you want to improve. This will help you understand whether educational content is needed at all, and if so, choose the right approach.
Here are some examples of goals:
- to increase conversion to lead
- to increase the number of users at the top of the funnel
- to decrease CAC
- to increase retention
- to increase sales of pro-subscription
When you have a goal, you can go deeper into problems that interfere with getting the result.
For example, you have a marketing SaaS service and want to increase conversion to lead. You need not just create educational content about your product, you need to analyse what the reasons are for low conversion to lead. It can be a wrong targeted audience, low perceived value, insufficient understanding of how to get results with the product.
To increase lead conversion you need to understand the main reasons for the problem and firstly work with them. Educational content is not a silver bullet. However, it can become a booster for your product.
Let’s see, what to do next.
Step 2. Analyze your audience
Before creating content, you need to understand the audience's needs. We need to understand the barriers, the pains, current and desired state of the audience. The audience should become a hero with our product.
Here are some ways to achieve it:
- Search for information on forums. This can be helpful at the start to find hypotheses.
- Conduct user interviews. It’s the way to understand users and get quality information from them.
- Conduct a survey. This can be helpful to check the data you get from user interviews.
Step 3. Create content
You need to connect users' problems and your product through content. You need to help the audience to solve their problems with your product.
There are a bunch of different types of content: e-books, blog posts, courses, podcasts, reports, and webinars. You should find a convenient way to connect with your audience.
Here we can draw an analogy with the “product-market-fit” framework, just in this case it will be more like a “format-channel” fit.
To understand what format is suitable, you can analyse:
- Lifestyle reports. It can be useful to explore reports at Global Web Index, Pew Research Center, Ipsos, Nielsen, GfK and other analytical companies.
- Competitors’ content. Here you need not blindly rely on competitors, but analyze what they have done and why.
- Your audience habits. During analysis of the audience, you can collect information about what content users consume, where they prefer to consume it and when.
Step 4. Promote content
There are 2 groups of users you want to promote content to — potential customers and existing customers.
Here you need to find your “format-channel” fit. For example, teens are unlikely to use email regularly and are more likely to consume content on YouTube, TikTok, and Instagram. To learn more about different networks, you can go on Statista.
For current customers, you can use owned media: links on your website and app, email newsletters and social media.
But to reach new people, you need to set up distribution on other channels. It can be paid, earned and shared media. To understand what channels would be better, you can try to prioritize them using the ICE score. You can read about this here.
Step 5. Get feedback
Educational content should be treated as a product: keep track of metrics, look for growth points.
On a small volume, it will be useful to conduct interviews with users; on large volumes, you can also look at metrics and conduct surveys.
Metrics can be divided into 2 groups:
1. Metrics for content evaluation
Let's say we have a free online course on how to use the service and solve users’ problems with it. There are 3 lessons in the course.
If users fall off on the first lesson, if only 10% reach the end, then something is going wrong. We need to think about whether we give value in this course, how clear and user-friendly it is.
Metrics are suitable here: reachability, time on the site.
2. Metrics to evaluate the impact of content on goals
When choosing metrics, you need to understand how content affects them. It is necessary to choose for evaluation those metrics that directly affect.
For example, our product has sales through sales managers. In this case, you should not take sales conversion as the main metric of educational content. Many factors can come into play here. It is better to take conversion to lead as a metric.
Metrics are suitable here: conversion to lead, amount of collected emails.
Step 6. Convert users to customers
Okay, you have an educational product, you educate the audience. Now we need to understand how to convert users into customers.
To do this, you need to reduce friction and increase perceived value. This is where trials, discounts, and the ability to return money can help.
You can work differently with users who take the product directly and who already use the free version.

Users from paid ads see less perceived value in the product than users from word of mouth. In this case, for paid ad users you can give a trial, and for referral users, you can give a discount.

You need to understand that low friction doesn’t guarantee you 100% converted users. That’s impossible. Some of the users don’t need paid product features. For example, a Google Drive user may have enough free storage of 5 GB and not need additional space for a surcharge.
Conclusion
Content marketing and user education aren’t investments into nothing. User training will help you to improve each stage of the funnel.
The main thing is to treat content as a product. Do this - not just to sell the product as soon as possible, but to help users. It turns out to be a win-win situation. Users solve their problems faster and more easily and you ... receive a new client.
