3 Types of Viral Loops: Growing Your Customer Pool [Part 2]
![3 Types of Viral Loops: Growing Your Customer Pool [Part 2]](/content/images/size/w1200/2022/12/137-1.png)
Have you ever wondered how some companies seem to grow so quickly? They have a product that is doing well, and then it just explodes. Is it a lucky coincidence, or is there a secret ingredient to their marketing campaigns?
Well, it’s neither, actually, because the lead-up is a well-defined and well-executed strategy, not a coincidence. And there’s no secret, not anymore, that at the center stage of this strategy is a viral loop.
A viral loop is a type of marketing technique that will help your company grow by increasing your customer pool, but how does it work? Let’s find that out based on three main types of loops.
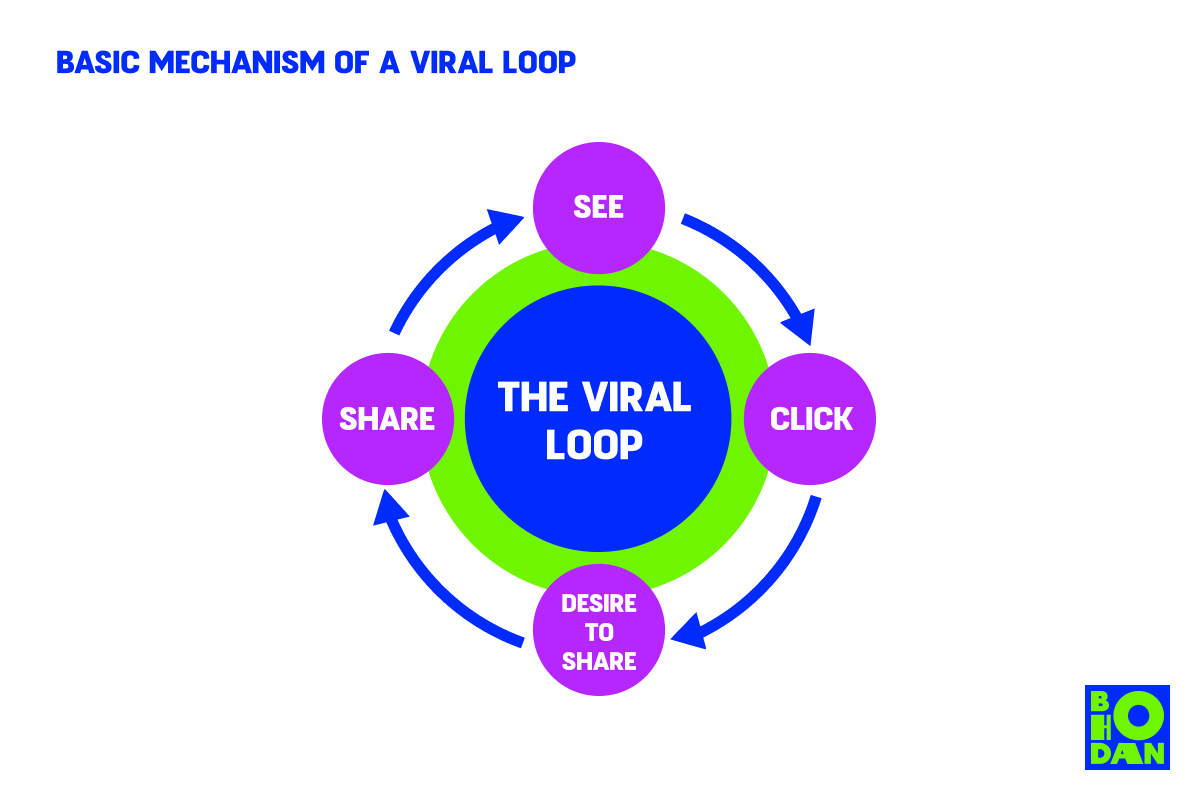
What Is the Basic Mechanism of a Viral Loop?
A viral loop is a marketing technique that encourages customers to refer new customers to the product or service. This can be done through incentives such as discounts, free products, or early access to new features. The goal is to create a system where customers are continually referring new users or buyers, which increases the customer pool and drives growth.
Viral loops are an effective way to drive growth and facilitate word-of-mouth marketing – a powerful tool for growing your business and expanding your customer base.
Types of Viral Loops
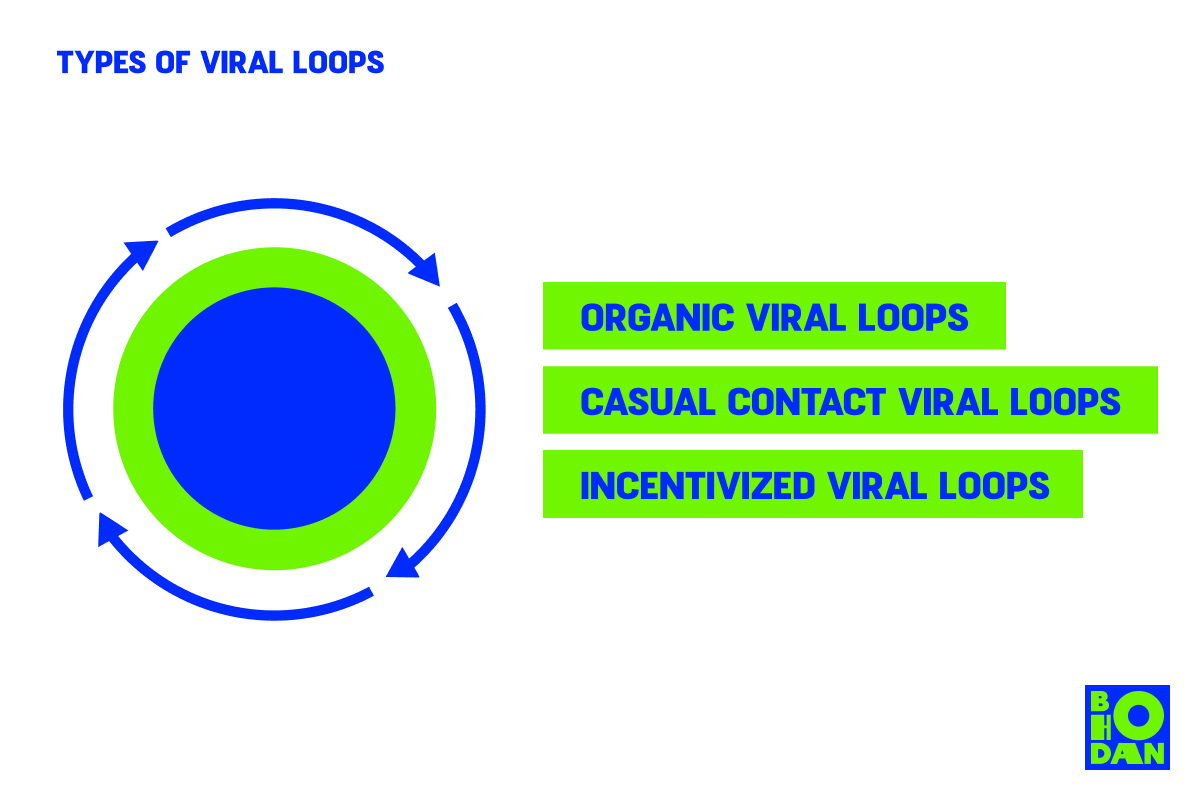
Viral loops can be divided into three main types based on the nature of a user’s contact with a product or service. So let’s discuss them in more detail and figure out what constitutes each type.
Organic Viral Loops
Organic loops mainly happen due to the word-of-mouth mechanism, but they also involve other factors. Such viral loops are built into products or services so users can easily share content with their followers, friends, fans, and family members through social media channels, like Facebook and Twitter.
Organic viral loops do not offer any incentives from the company's end aside from the product. But users are naturally motivated to share content with their friends and followers, without any rewards or induced motivation from the organization creating the product or service.
Several factors facilitate organic viral loops:
- Word of Mouth – Users talk about a product or service to their audience (friends, family, coworkers, followers, etc.).
- Content Virality – Users share entertaining, informative, or valuable content on social media.
- Inherent Virality – Users gain value when other people sign up (e.g., for Instagram or Facebook) because their connections grow.
- Collaboration – Users are encouraged to work together to achieve a common goal. For example, in Trello, a task management tool, users can invite others to collaborate on tasks by sharing a special link.
- Communication – Users are also encouraged to communicate with each other on a social networking platform. For example, Slack is meant for communication between many people, which means more people need to join in order for that to happen.
What Constitutes an Organic Viral Loop?
- Nature of the trigger. In order for any type of viral loop to work, there have to be easy steps and simple actions so users can do what is required without much effort.
- Trigger frequency. The more frequently a user gets exposed to triggers, the better their chance of action (though it shouldn’t be so frequent it’s spammy).
- Response rate. It's not enough for the trigger frequency to be high, as many triggers often result in no response from users who may have been exposed to them several times. Then, the response rate is the percentage of users who take action after being exposed to a trigger.
Casual Viral Loops
These are viral loops based on the idea of a customer introducing your brand to another person who would become interested in it. These loops typically don't involve any direct incentives but rather rely on marketing efforts that encourage customers to bring their friends, family members, or coworkers onto the platform because they think those people will enjoy it too.
These loops can be subdivided into three categories:
- Embedded Loop. A company embeds a viral loop into its product or service, which means users must be brought onto the platform in order for it to work.
- Physical Content Loop. As the name suggests, users are encouraged to share physical content with one another, which leads to an increase in their social networks/friends lists and allows them access to more people on the platform.
- Awards Loop. This is where users introduce products to a broad audience with awards, certifications and etc.
What Constitutes a Casual Contact Viral Loop?
- Branching. For the best results, there has to be a high branching factor, which means users need to be able to communicate with a whole lot of people at the same time.
- Time. If it takes longer for someone who has been exposed to a trigger to join the platform, it’s less likely they will join.
- Ripple Effect. It's what happens when a user refers someone to the platform, and they take action. This creates a ripple effect where more people are exposed to the brand and start taking action as well.
Incentivized Viral Loops
As the name suggests, incentivized viral loops involve providing rewards or incentives to users to get their friends and followers onto the platform. These loops are often based on referral marketing programs, such as the ones used by companies like Uber.
Incentivized viral loops rely on a reward system, so they usually only work for products or services with a low cost to entry, as customers need to be convinced about their value before they're willing to go out and encourage their friends and family members to sign up too. There are three types of incentives used for this type of viral loop:
- Money: This is where people are paid for getting their friends and followers to join the platform.
- Content: Some platforms offer exclusive access or additional content to users who get their audiences to join.
- Features / Product Access: Some platforms offer exclusive features or product access to users who get their audiences to join.
What Constitutes an Incentivized Viral Loop?
- Meaningfulness. This involves making sure people understand why the incentive will be of value to them. The more meaningful it is, the better the results will be.
- Alignment. This means having a strong alignment between users on both sides of the loop (existing and potential), which can happen when there's a mutual benefit or some kind of symmetry.
- Positioning. This is about making sure that people are aware that the platform exists in order to get them involved in the incentivized viral loops.
Types of Rewards
Different types of rewards are provided by the different types of viral loops. These include:
- Free products – a product that is given away for free, such as when Dropbox gives away extra storage for referring new users
- Internal currency – different types of currency that can be earned within the product itself
- Discounts – a discount from your company on a partner company’s products (Zola, for example, allows people to save money by buying gifts from other businesses that are registered with them.)
- Company swag – free or branded merchandise offered by a company on a larger scale
- Exclusive content – content offered by a company to its customers exclusively through methods like email newsletters, videos on YouTube channels, or access to certain events
- Early access – when a product allows people to have early access or beta keys for certain products that are still in development (This practice can easily be abused by companies, so it needs to be monitored carefully.)
- Access to private communities – allowing customers to join exclusive forums and groups that can provide them with new insights and opportunities
While the different types of viral loops have different incentives, triggers, and rewards, they all intersect in one way or another. So, to add some clarity to the meaning of each type, let’s review some real-life viral loop examples.
Organic Viral Loop Examples
Communication: Slack
Slack is an online, business-oriented chat app that makes collaboration easy. It's super simple to use, and it facilitates keeping track of all the important conversations happening in your workplace.
Slack is made up of channels that work like chat rooms. You can create as many channels as you want, and each one can focus on a different topic or project. Within each channel, you and your coworkers can have a conversation by typing in the text box at the bottom of the screen.
There’s one “but,” though — you need to be invited into a business’s workspace.
Slack's Value Proposition
- Collaboration and transparency: Slack makes it easy for coworkers to communicate with each other and see what everyone is working on. This helps keep projects moving forward and eliminates the need for constant status updates.
- Integrations: Slack integrates with tons of other apps you probably already use at work, like Dropbox, Google Drive, Zendesk, and 1000 more. This makes it easy to send important files directly from one app to another without having to jump back and forth between different programs.
Steps to Achieving an Organic Viral Loop
There are several steps that encourage users to complete the loop, but the target audience is mostly business owners and managers who are willing to create a workspace and invite coworkers:
- See an ad – sign up for the product. Slack uses social media to push organic traffic to its website and generate new users. Third-party integrations also push organic traffic to their website. Slack also has a referral program that lets you earn credit for inviting your friends to sign up.
- Invite teammates. When someone signs up for Slack, they invite their coworkers.
- Recommend. After using Slack, a coworker might refer a friend to share their positive experience with Slack or create their own workspace. Of course, then they add new users.
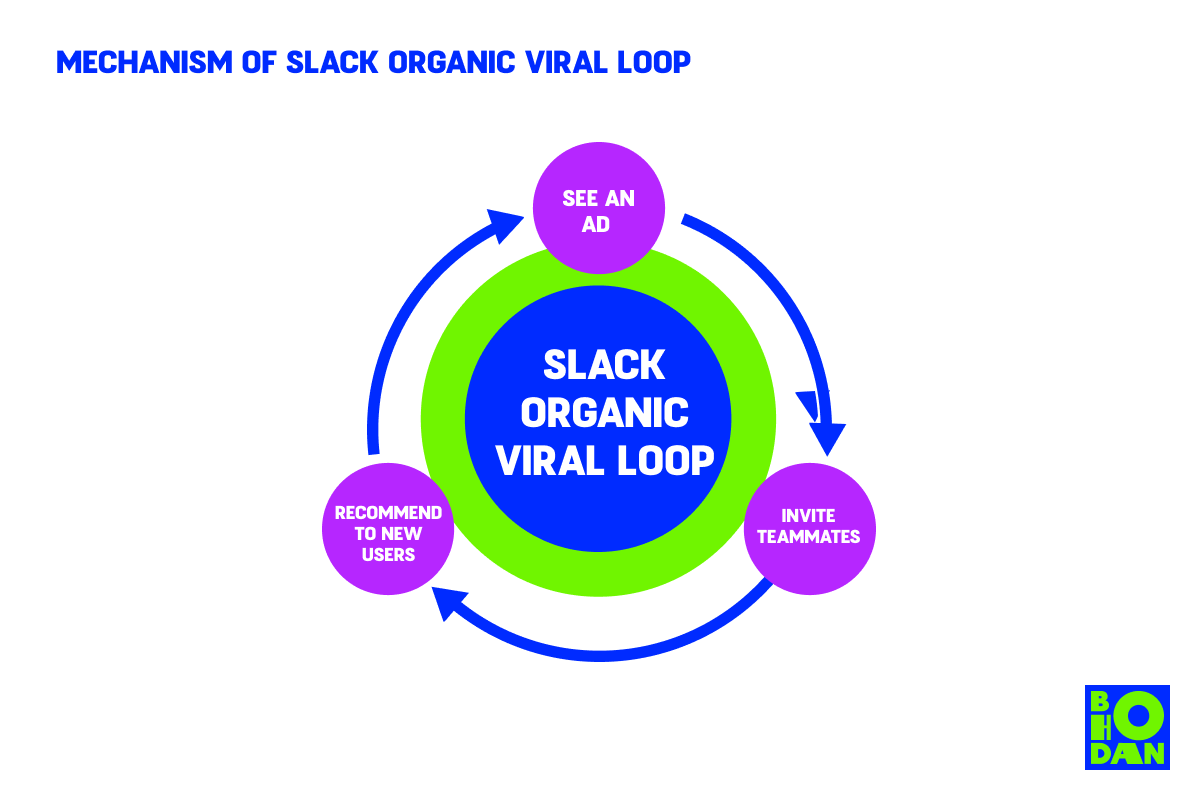
The more people use Slack, the more likely it is to continue growing its customer pool. And that's a good thing for businesses looking for better ways to collaborate.
Want to read full article with examples from Figma, Reface, Typeform and Doordash? Subscribe to my blog (it's free) 👇
Collaboration: Figma
There’s no doubt that Figma is an essential tool, as product design goes way beyond designers alone. The rest of the company or team also should or have to chip in, so Figma offers an interface where designers, developers, product managers, and other professionals can collaborate.
The web app offers a variety of fonts, tools for creating vector graphics, the ability to add stock or custom imagery, prototyping options, and more. But what sets it apart from a dozen other graphic design tools? It’s the fact that other people can view and contribute to the process – that is, the essence of collaborative tools.
Figma’s Value Proposition
- Web-first format. The tool doesn’t just offer cloud storage; it lives in the browser interface. This way, all collaborators who have access permissions to a graphic, layout, or prototype can view or edit the design.
- Open product discussion. Collaborators can leave feedback and improve the product design together. Moreover, they can refer to the version history to review any changes.
- Elimination of extra work. Creating and approving a design involves more than just editing it and uploading the new version to the cloud. It also requires messaging about changes and making sure the feedback is clear. The in-browser experience eliminates such tedious steps, leaving pure collaboration on a design at hand.
- Everyone on the team can chip in. Since multiple people can view and work on a design at the same time (no need to re-send or re-upload a file), virtually all team members can provide feedback and help with improvements.
Steps to Achieving an Organic Viral Loop
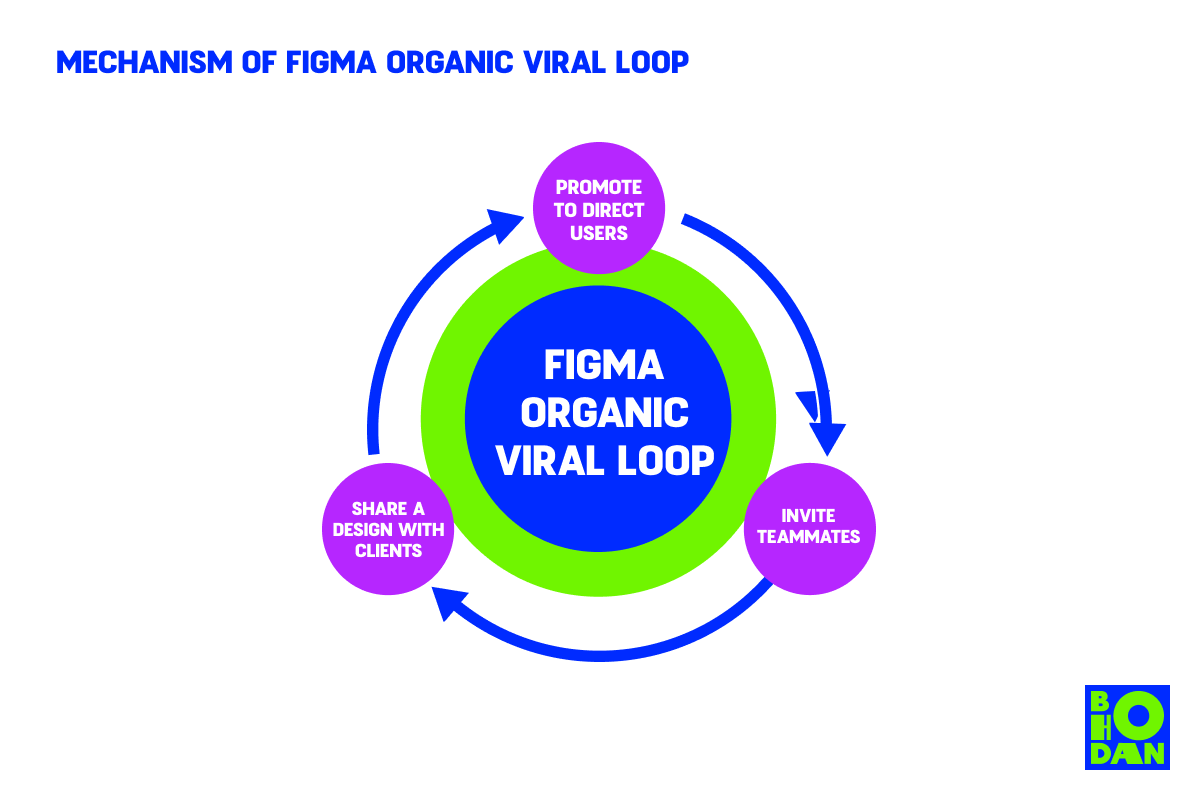
The key to Figma’s virality isn’t just the necessity of such a product. It’s a browser-first application that simulates real-life design-making processes as you would experience in a team meeting.
- Get designers on board. Think of how many versions of the same file designers have to send back and forth before a final one is approved. So when they see an ad for a platform that allows them to edit designs in the cloud, not just store them in the virtual space, they’re bound to try such a handy product. So Figma’s initial distribution is among designers.
- Get the rest of the team on board. Say the design is for an app and requires a copywriter’s input. They can add the necessary text to the design without the back and forth messaging. Thus, the whole team will see the benefit of collaborating in-browser.
- Share the design via a link. A PM can send a link with the complete design to a client without the need for the client to register or subscribe to Figma. This way, information about Figma as a product is shared with new potential users.
Thus, Figma’s loop starts at the designer, spreads to the non-designer part of the team, sweeps the whole company, and continues its growth to other companies (via clients) that are located globally. Well, thank goodness for remote work and outsourcing.
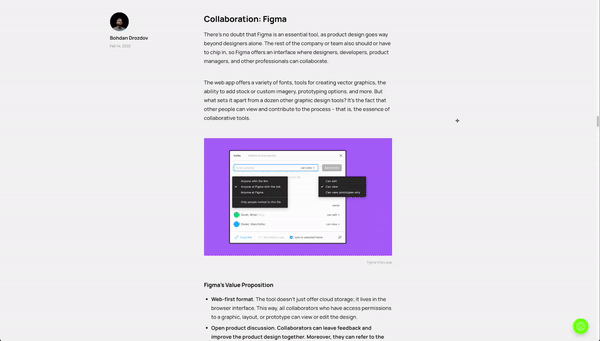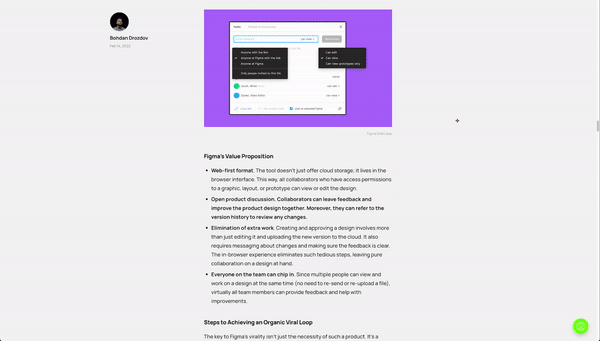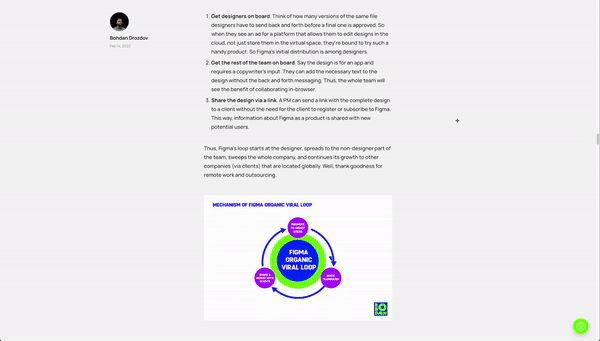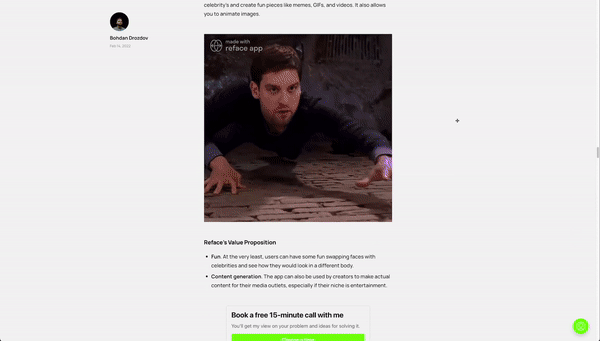
Content Virality: Reface
Reface is a content generation app where you can swap your face with a celebrity’s and create fun pieces like memes, GIFs, and videos. It also allows you to animate images.
Reface’s Value Proposition
- Fun. At the very least, users can have some fun swapping faces with celebrities and see how they would look in a different body.
- Content generation. The app can also be used by creators to make actual content for their media outlets, especially if their niche is entertainment.
Steps to Achieving an Organic Viral Loop
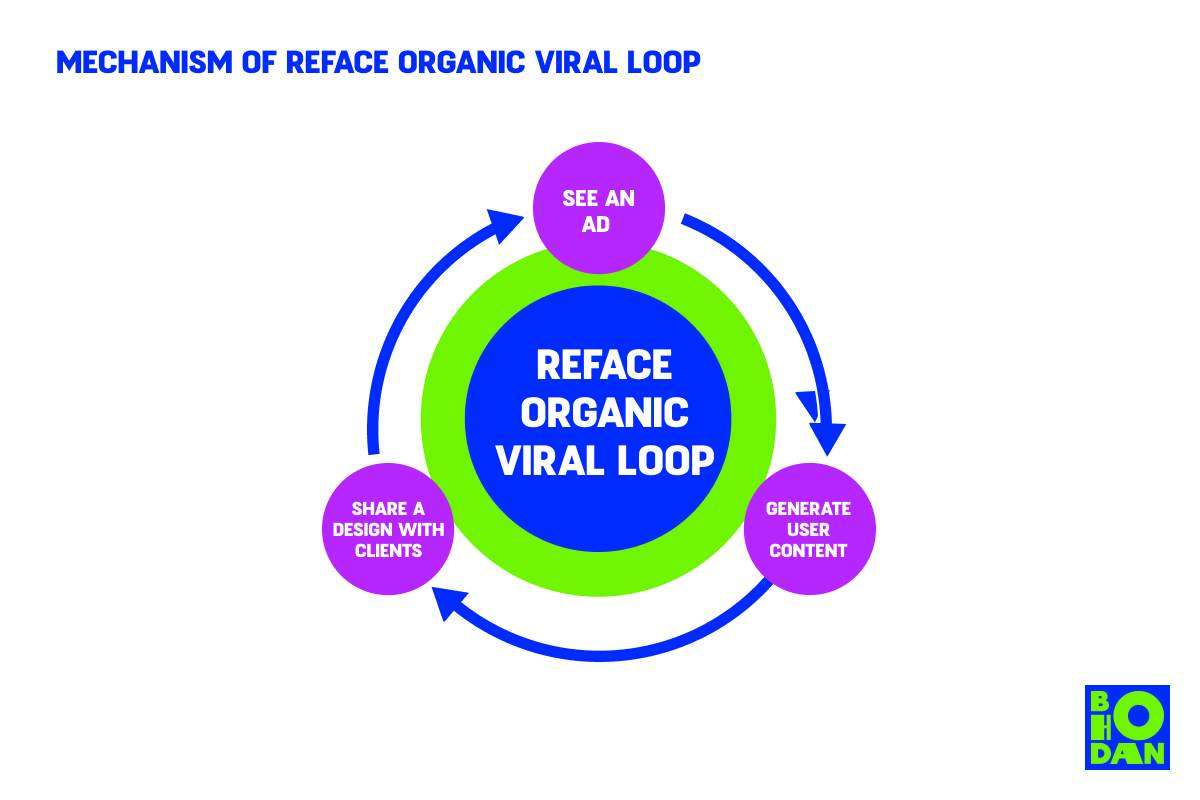
Reface has turned a complex AI algorithm into an amusing experience for content consumers. The key to its popularity growth is implemented in the app itself.
- See an ad – install the app. What’s interesting about the advertising here is that new users can come across more than just a marketing ad on social media or a tech news article. Reface’s generated content has a watermark (in the free version), so potential users could also come across the app’s output.
- Create a piece of content with your face on it. Users can browse the app’s library of photos and videos or upload an image from their phones. Then, they can swap faces with the characters, animate, and add text, adding originality to the piece.
- Share with friends and followers. The app offers standard sharing options to social media and chats. This is likely to motivate new users to install the app for a similar experience.
Casual Loop Examples

Embedded Loop: Typeform
Typeform is a platform for creating custom forms and collecting data. It doesn’t require any technical knowledge to customize a good-looking form using templates, and you can then integrate the data with your CRM system.
Typeform Value Proposition
- Simple form builder. If you’ve ever used a presentation tool, Typeform is pretty similar. You can choose a ready template or build a form from scratch using different layouts and design features.
- Interactive forms. Users receive one question at a time, which creates a more interactive experience.
- Integrations. Typeform integrates with 120+ apps, including Slack, Zapier, and HubSpot. So you can create a quiz or a feedback poll and send it to colleagues or clients via the integrated platforms.
Steps to Achieving a Casual Contact Loop
Typeform gets exposure just from people filling out a survey or questionnaire, so the mechanism of this loop is pretty simple. The rest is providing an actually good modern product.
- First contact. Users come across an ad, research form builders, and see Typeform on the list, or simply come across the form builder among integrations.
- Exposure. Respondents fill out a form and see the phrase “Powered by Typeform” – they are likely to click on it or simply remember the provider, especially when they’re exposed to it frequently.
- Onboarding. Signing up to Typeform is an interactive process – you complete a form, provide an email address, and get to the form builder that helps create your first form with a set of onboarding tips. This ensures that users stay on the platform long enough to try out the product.
An interesting fact about Typeform is that they measured ten variations of the landing page that the phrase “Powered by Typeform” redirects to, and only one of them provided a 200% CTR.
Physical Content Loop: DoorDash
DoorDash is a food delivery service that allows you to place orders online. It brings together restaurants — and other food providers — and delivery drivers and connects them to patrons via a mobile app.
While delivery services were always attractive among clients – you get restaurant food at home without having to go out – they became especially popular among food providers during the pandemic. Why close your services if you can keep feeding people at a safe distance?

DoorDash’s Value Proposition
- Variety of food options. As opposed to restaurant delivery, DoorDash provides you with a choice of local restaurants, cafes, and grocery stores. This makes a client’s search for a good meal much easier.
- No need for native delivery services. Having its own delivery drivers isn’t always a cost-effective option for a business, unlike utilizing a third-party service.
- Mobile app. Placing an order from a mobile app is usually more convenient than looking for a website and making a call.
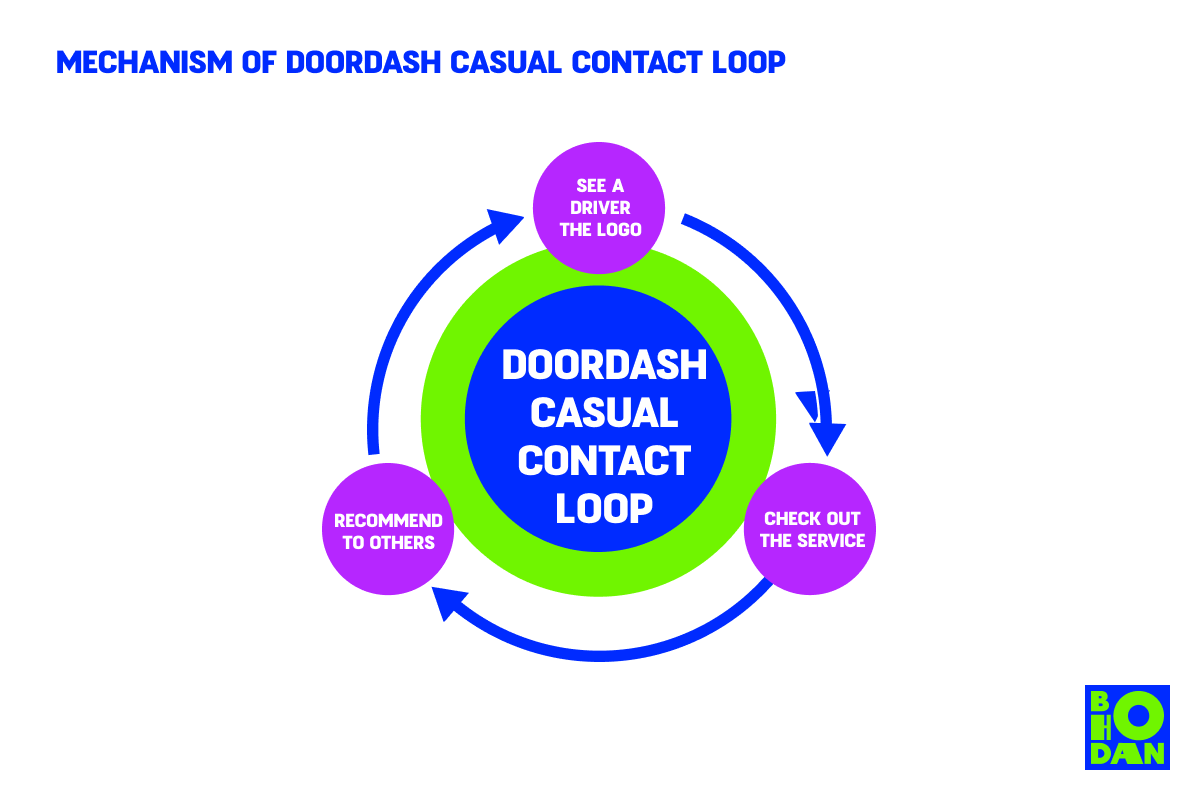
Steps to Achieving a Casual Contact Loop
Why people take interest in DoorDash is pretty obvious – they see drivers all over their cities, as well as ads online. Yet it is the fastest-growing food delivery service, besting Grubhub, Uber Eats, and Postmates even before the pandemic.
One of the causes is that DoorDash purchased Caviar, a higher-end delivery service. But there’s more.
- Increase in coverage. DoorDash partners with food places that don’t offer their own delivery to reach more patrons, including via these places advertising the delivery collaboration.
- Physical advertising. People see delivery vehicles with the logo and are encouraged to check out the service.
Awards Loop: G2
G2 is a peer review website where you can find reviews, ratings, and social data about software and SaaS solutions. It’s a great place for businesses to find out what real users think of their products, but also for users to find suitable solutions – all based on authentic feedback.
G2’s Value Proposition
- Product comparisons. Users can compare the pros and cons of two apps to decide which one is more suitable.
- Easy search. G2 has over 100 categories of software and services in case you don’t yet have exact candidates, as well as a simple search.
- Trustworthiness. It is more likely that users don’t gain anything from posting a review on a site like G2 than on a forum, community, or the official website.
- G2 referral. Companies can see how many users opened their websites from G2.
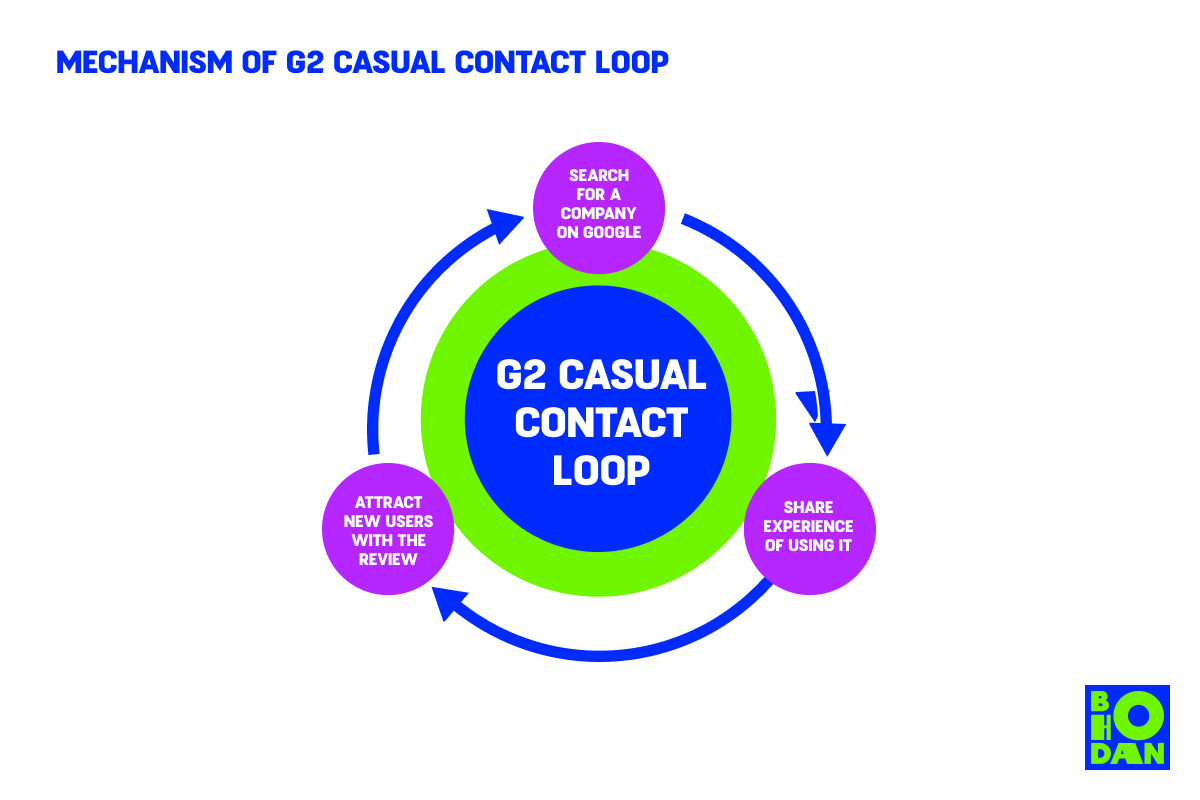
Steps to Achieving a Casual Contact Loop
Screening peer review websites is an inextricable part of the software and services shopping experience, yet G2 isn’t the only platform that offers feedback. So what are they doing to achieve a loop?
- Targeting different user categories. The marketing team at G2 is divided into several departments that focus on the acquisition and motivation of buyers (those who are interested in software or services), sellers, and reviewers. For example, having a piece of software listed on the platform means that users are likely to find it among the top results when looking for reviews on that software.
- Users share their experiences. G2 users share their own experiences about a business, which can be positive or negative. These reviews can also be shared on LinkedIn.
- G2 uses those reviews as a valuable asset. The information gathered from user feedback is then used to determine the overall score for businesses and other relevant factors that will affect another user’s decision-making process.
- Users are influenced by company ratings on G2. The better the rating, the more likely people are to visit the company’s website and try out their product.
Incentivized Viral Loop Examples
Money: Cash App
Cash App is a mobile application for monetary transactions that allows users to transfer money from one account to another, use a virtual card for debits and deposits, and invest in Bitcoin and stocks.
Cash App’s Value Proposition
- Security features. The app uses encryption and verification locks to ensure the safety of user transactions.
- Customizable debit card design. Users can add personal swag to the virtual card and use it for everyday spending. The custom design option is free.
- Low investment threshold. Users can start investing with as little as one dollar, which is ideal for those who want to try it out but don’t have relevant experience.
Steps to Achieving an Incentivized Viral Loop
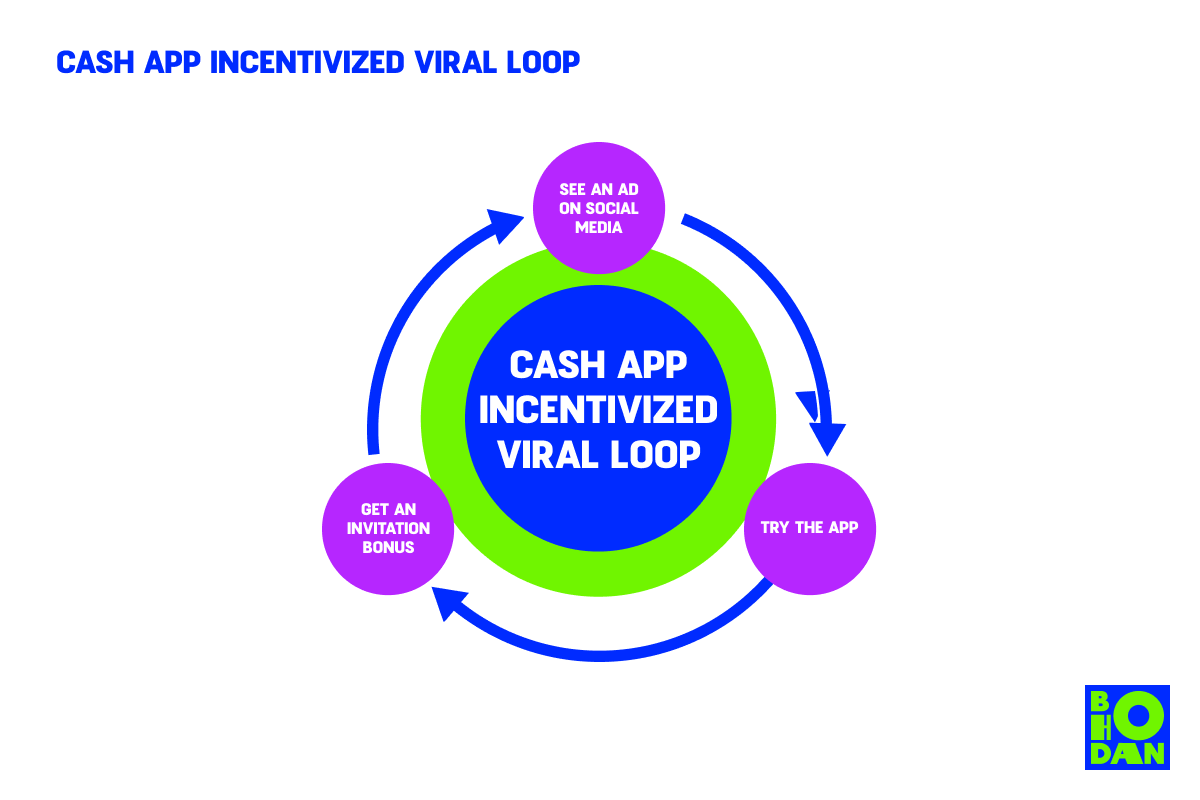
You should be looking for your audience where they like to hang out the most. Cash App knows that people who are more open and interested in a product like this will likely be on social media, and that’s where engagement usually sparks for the product.
- Social media coverage. The app holds a weekly marketing campaign on Twitter where users have a chance to win free cash if they retweet the campaign post with a special tag. That’s a good incentive to install the app.
- Influencer referral. Cash App used TikTok – the home of viral videos – to get a song about their app trending and gained over 156 million views, which definitely increased the brand's familiarity among potential users.
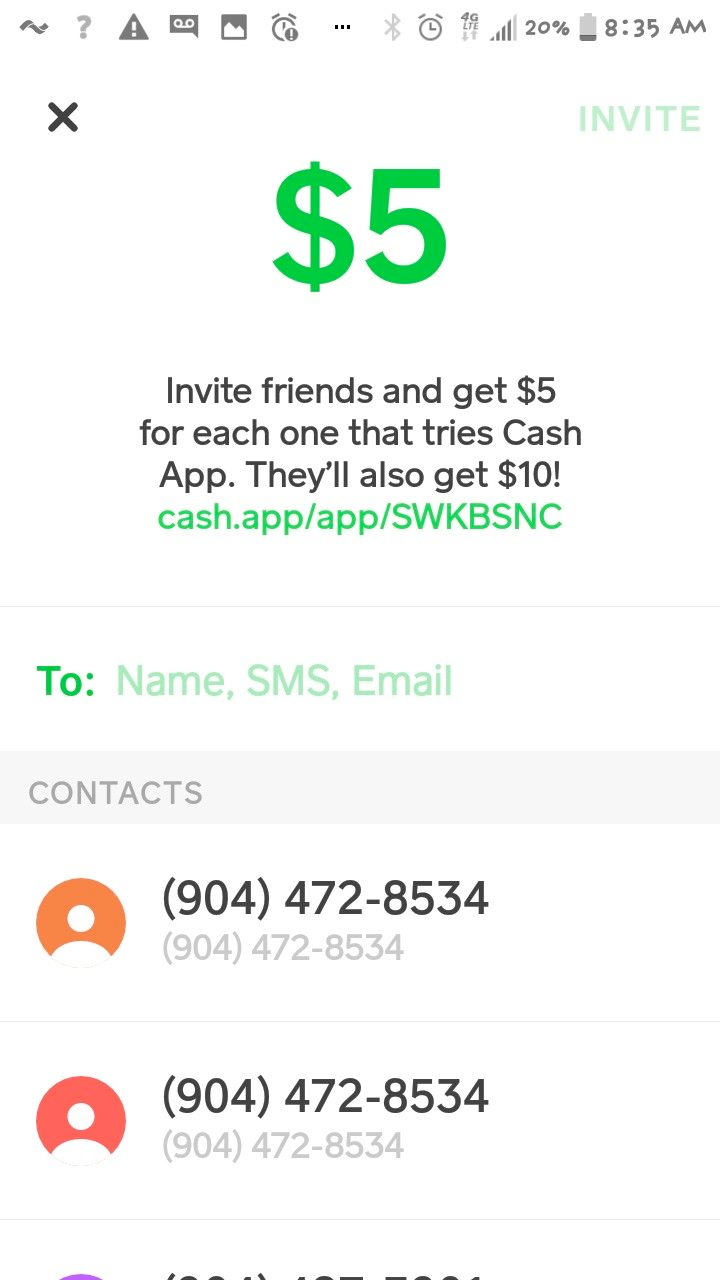
- Invitation bonuses. Existing users of the app can invite friends and earn five dollars or more for each new account.
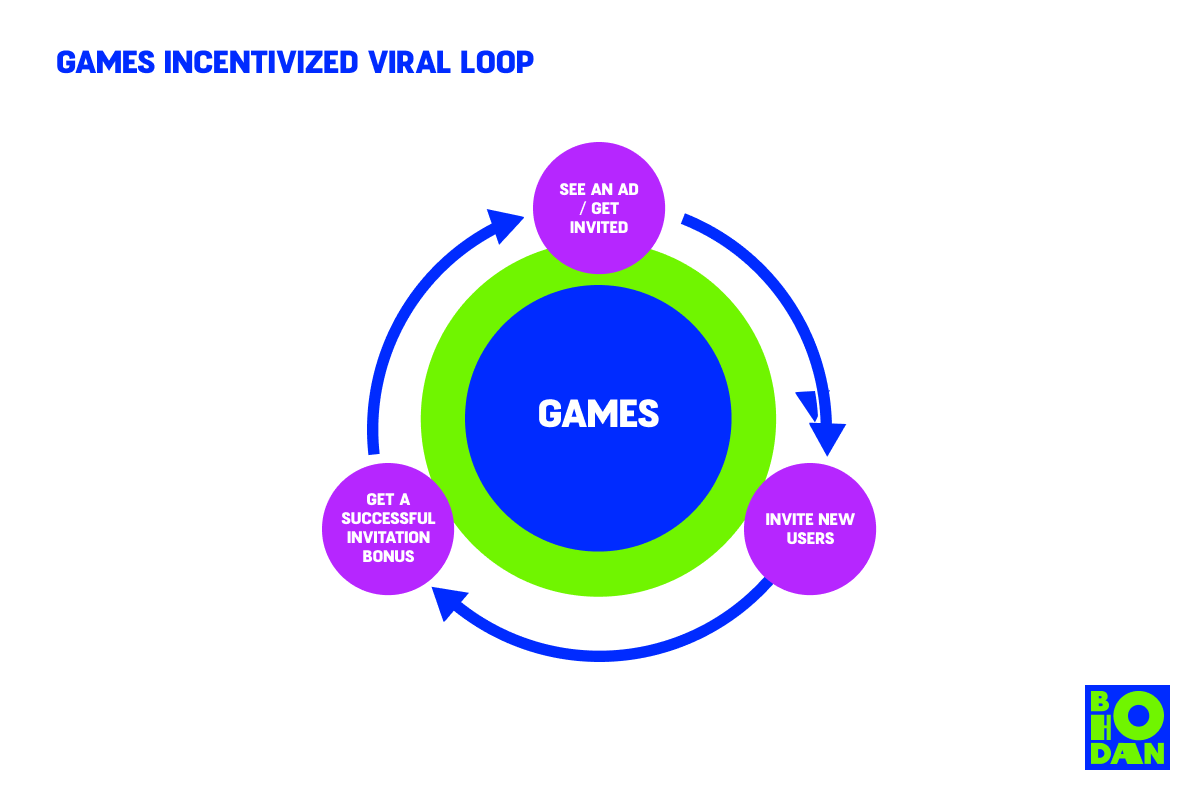
Content: Games
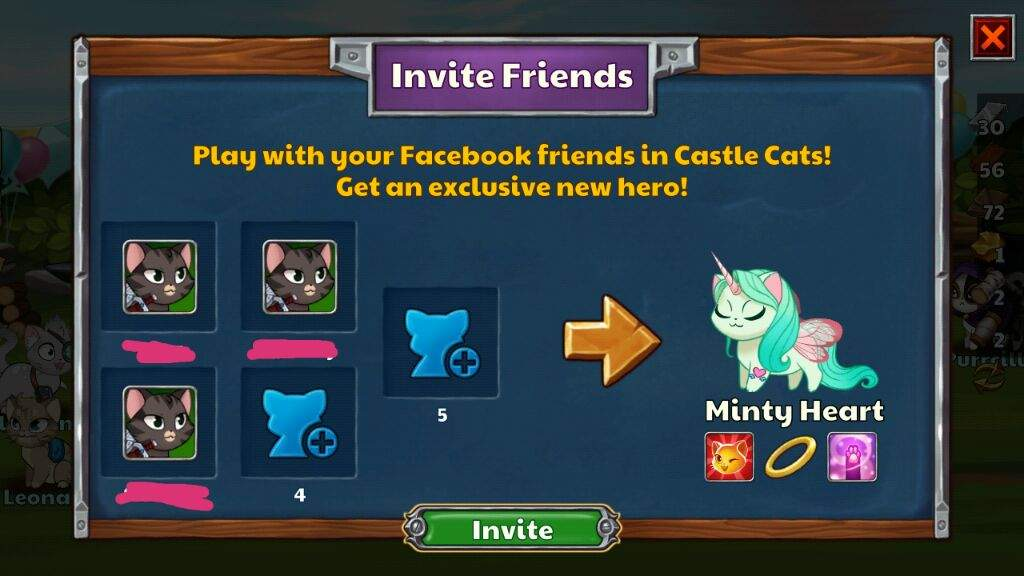
With games, it’s relatively easy to create a viral loop. As long as the game itself is engaging and fun, the loop mechanism is pretty standard. Usually, it’s about sending invitations for other people to join the game to help the first user achieve milestones. It could also be allowing users to generate content based on the game – for example, Castle Cats.
Value Proposition
- Rewards. They are always one of the biggest incentives for acting on behalf of a product and can act as a sort of payment for the favors users do.
- Shared experience. Adding your friends as players means you can enjoy the game together.
Steps to Achieving an Incentivized Viral Loop
It’s not uncommon for games to have a feature where users can invite friends, but there’s not much incentive in sending perks to each other. Instead, Castle Cat provides a definite win to players who can fulfill the rules:
- Friendship cat – users need to get five new players to use their invite link and install the game.
- Chest of game currency – users can earn perks once a week if a new player installs the game.
It’s quite obvious that if you want five people to actually install a game or even one person a week to sign up, you need more invites to make sure this happens. Naturally, users will invite more people than required to boost their chances, increasing the game's outreach.
Features/Product Access: Blind
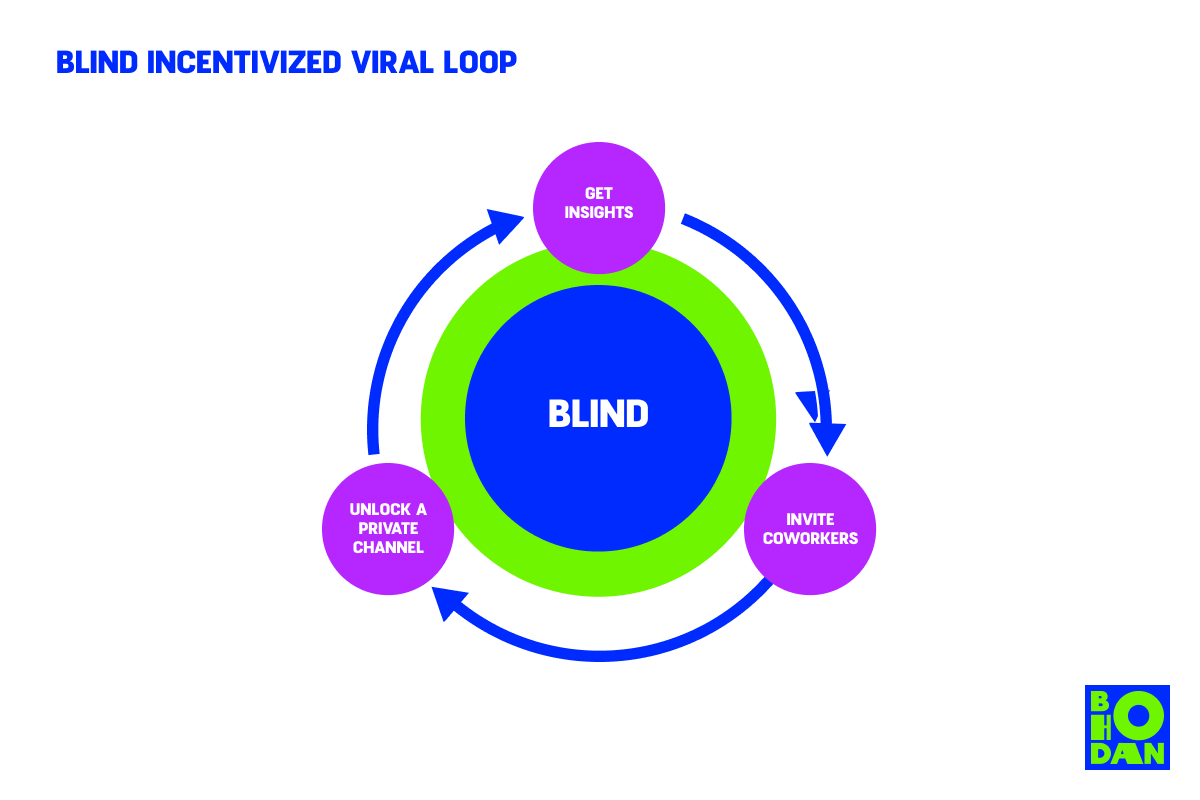
Blind is a networking platform where users can share anonymous reviews about their company, as well as salaries and interview experiences. It has more than five billion users.
Value Proposition
- Private chat. Users can create private chats with colleagues to talk about their company.
- Expanding community. The platform allows users to build new professional connections.
- Professional advice. Users can get tips from the community on interviews and salary negotiation via direct messages with company employees.
Steps to Achieving an Incentivized Viral Loop
Blind offers quite a unique product – a mix of Slack, LinkedIn, and Reddit – where professionals can voice their opinions or concerns without feeling judged.
- Providing insight. Blind allows professionals to peek inside a company and its employees’ unfiltered views.
- Incentivizing private channels. One way Blind motivates users to complete the loop is by offering a private company channel for 30+ coworkers. If users want that, they are encouraged to invite new users from their company.
- Providing a two-way incentive. Both the referrer and the new user earn value from registering. This comes in the form of exclusive content and the feeling of being part of a group.
Blind isn’t the only platform that offers an incentive to both referrers and new users. You can also find the same mechanism in apps like Robinhood, Venmo, and Interactive Brokers.
Conclusion
A viral loop is a technique that promotes continual growth by generating organic, casual, or incentivized referrals. It's how you get your current consumers to recommend your brand to others and those new customers to tell even more people about you. It helps you ensure steady growth by obtaining highly qualified leads.
Many products can use a few different types of viral loops at the same time since the loops are not mutually exclusive. To establish a successful viral loop, you'll need to figure out what kind of material your customers value, offer an incentive for them to spread it, and take a few more steps.
